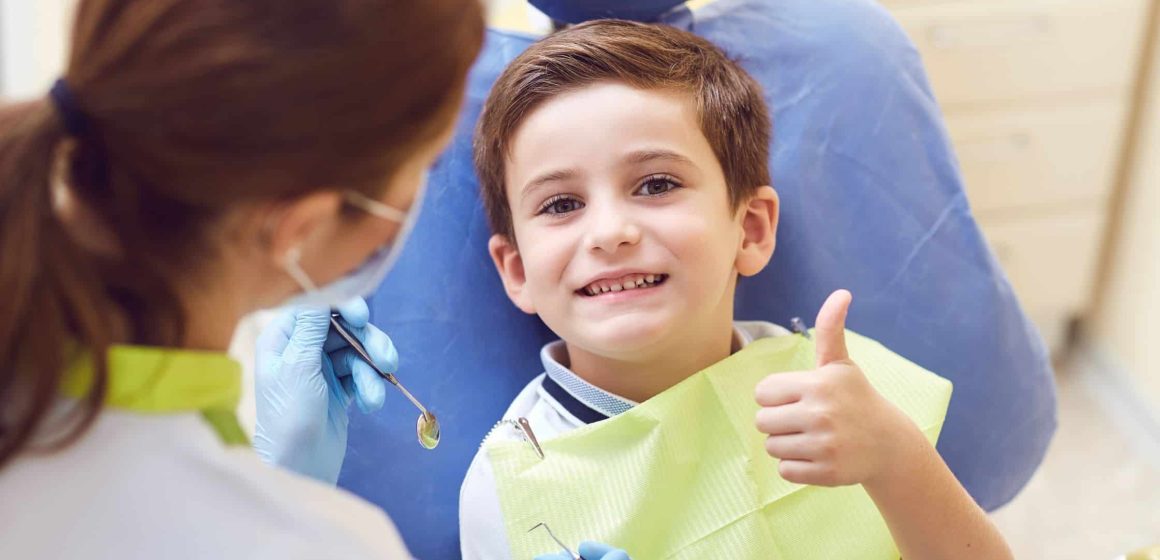
Ensuring your child has a healthy smile begins with early dental care. Pediatric dental visits play a crucial role in preventing tooth decay and promoting good oral hygiene habits. Early dental visits set the foundation for lifelong dental health. This guide explains the importance of early dental visits and provides tips on keeping your child’s teeth healthy from the start.
The Importance of Early Dental Visits
Early Detection and Prevention: Regular dental visits allow dentists to detect potential issues early, such as tooth decay, gum disease, and bite problems. Early detection can prevent minor issues from becoming major dental problems.
Establishing Good Oral Hygiene Habits: Pediatric dentists educate parents and children about proper oral hygiene practices, including brushing, flossing, and healthy eating habits. Establishing these habits early can lead to a lifetime of good dental health.
Preventing Tooth Decay: Tooth decay is the most common chronic disease in children, but it is largely preventable. Early dental visits help prevent cavities through fluoride treatments, sealants, and professional cleanings.
Building Comfort with Dental Visits: Introducing your child to the dentist at an early age helps them become comfortable with dental visits. This can reduce anxiety and fear associated with dental appointments, making future visits more pleasant.
Monitoring Dental Development: Early dental visits allow dentists to monitor the development of your child’s teeth and jaw. They can identify and address any developmental issues early, ensuring proper growth and alignment.
When to Schedule the First Dental Visit
The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (AAPD) recommends scheduling your child’s first dental visit by their first birthday or within six months after the first tooth erupts, whichever comes first. Early visits are crucial for establishing a dental home and beginning preventative care.
What to Expect During the First Dental Visit
Introduction and Examination: The first visit is usually short and involves little treatment. The dentist will examine your child’s mouth, gums, and teeth to assess their oral health and development.
Oral Hygiene Education: The dentist will provide guidance on proper brushing and flossing techniques, as well as tips for maintaining good oral hygiene at home.
Diet and Nutrition Advice: The dentist will discuss the impact of diet and nutrition on oral health. They will provide recommendations for healthy eating habits that promote strong teeth and gums.
Discussion of Habits: The dentist may ask about your child’s habits, such as thumb sucking or pacifier use, and provide advice on how to address these behaviors if necessary.
Fluoride Treatment: Depending on your child’s risk of tooth decay, the dentist may apply a fluoride treatment to help protect their teeth from cavities.
Tips for Keeping Your Child’s Teeth Healthy
Start Brushing Early: Begin cleaning your baby’s mouth even before their first tooth appears. Use a soft, damp cloth to wipe their gums. Once teeth start to come in, use a small, soft-bristled toothbrush with a smear of fluoride toothpaste.
Brush and Floss Regularly: Brush your child’s teeth twice a day for two minutes each time. Floss daily to remove food particles and plaque from between the teeth.
Use Fluoride Toothpaste: Fluoride helps strengthen tooth enamel and prevent cavities. Use a rice-sized amount of fluoride toothpaste for children under three and a pea-sized amount for children aged three to six.
Limit Sugary Foods and Drinks: Sugary foods and drinks can lead to tooth decay. Limit your child’s consumption of sweets, juices, and sodas. Encourage healthy snacks like fruits, vegetables, and cheese.
Avoid Bottles at Bedtime: Putting your child to bed with a bottle can cause tooth decay. If they need a bottle at bedtime, fill it with water instead of milk or juice.
Encourage Drinking Water: Water helps rinse away food particles and bacteria. Encourage your child to drink water throughout the day, especially after meals and snacks.
Regular Dental Visits: Schedule regular dental check-ups every six months or as recommended by your dentist. Consistent visits help maintain your child’s oral health and catch any issues early.
Addressing Common Dental Concerns
Thumb Sucking and Pacifier Use: Prolonged thumb sucking and pacifier use can affect dental development. Encourage your child to stop these habits by age three. Your dentist can provide strategies to help.
Teething: Teething can cause discomfort and irritability. Use a clean finger or a teething ring to gently massage your child’s gums. Avoid teething gels with benzocaine, which can be harmful to young children.
Dental Injuries: If your child experiences a dental injury, such as a knocked-out or chipped tooth, contact your dentist immediately. Quick action can often save the tooth and prevent further damage.
Conclusion
Early dental visits are essential for setting the foundation for your child’s oral health. By starting dental care early, you can help prevent tooth decay, establish good oral hygiene habits, and ensure your child feels comfortable with dental visits. Remember to schedule regular check-ups and practice healthy dental habits at home to keep your child’s smile bright and healthy.
For more information on pediatric dental care and other health topics, visit the American Academy of Pediatrics – HealthyChildren.org.