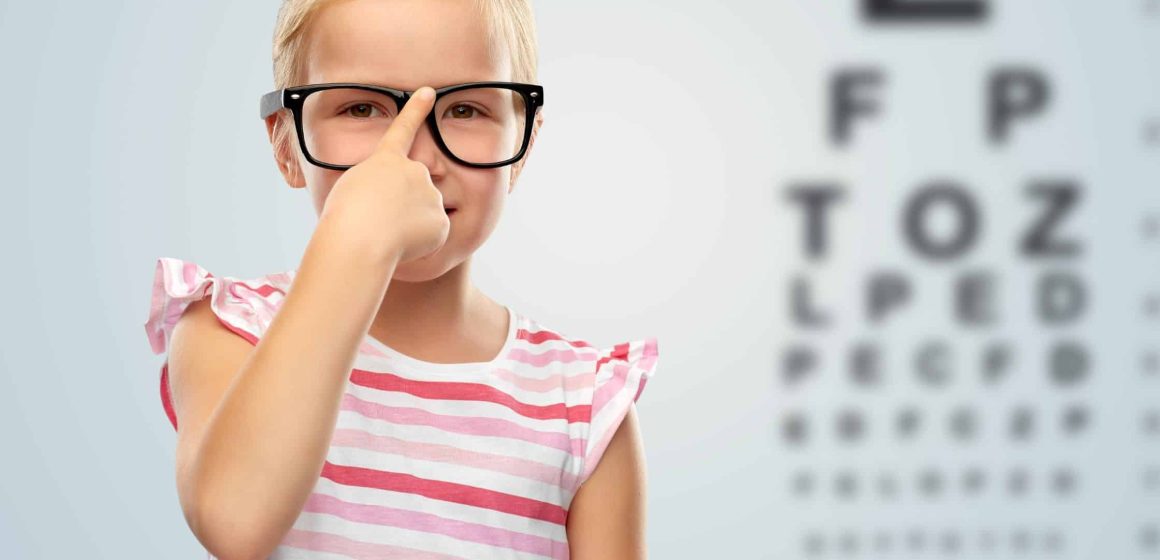
Good vision is essential for a child’s overall development and success in school. Routine eye exams are crucial for detecting and addressing vision problems early on. Regular eye exams can help ensure that your child’s vision health is on track, contributing to their academic performance, physical activities, and overall well-being. This guide explains the importance of routine eye exams for children and provides tips on maintaining optimal eye health.
Why Routine Eye Exams Are Important
Early Detection of Vision Problems: Many vision problems can be detected early through routine eye exams, even before a child shows any symptoms. Early detection allows for timely intervention, which can prevent more severe issues and support better vision development.
Preventing Learning Difficulties: Vision problems can significantly impact a child’s ability to learn and perform in school. Difficulty reading the board, seeing the text in books, or focusing on close-up tasks can lead to academic struggles. Regular eye exams help ensure that vision issues do not hinder your child’s learning.
Monitoring Eye Health: Eye exams are not just about vision correction; they also involve a thorough check of the overall health of the eyes. This includes checking for signs of eye diseases and conditions such as amblyopia (lazy eye), strabismus (crossed eyes), and refractive errors (nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism).
Promoting Healthy Development: Clear vision is crucial for a child’s physical development, coordination, and spatial awareness. Routine eye exams help ensure that your child’s vision supports their overall development.
Recommended Schedule for Eye Exams
Newborns: Newborns should have their eyes checked for any signs of congenital issues or other problems soon after birth.
Infants (6 months): By six months of age, infants should have a comprehensive eye exam to ensure their eyes are developing properly and to check for any early signs of vision problems.
Toddlers (3 years): At around three years old, children should have another eye exam to assess visual acuity and check for issues like amblyopia or strabismus.
Preschoolers (5 years): Before starting school, children should have a complete eye exam to ensure they can see clearly at all distances and have no undiagnosed vision problems that could affect their learning.
School-aged Children (6-18 years): Once in school, children should have annual eye exams to monitor their vision health, especially as they grow and their eyes continue to develop. This is crucial for catching any changes in vision that could impact their academic performance.
Signs Your Child Might Need an Eye Exam
While routine eye exams are essential, there are also signs that may indicate your child needs an eye exam sooner:
- Squinting or closing one eye
- Tilting their head to see better
- Holding books or objects very close to their face
- Frequent rubbing of the eyes
- Complaints of headaches or eye strain
- Difficulty reading or frequent loss of place while reading
- Excessive tearing or blinking
- Sensitivity to light
- Poor hand-eye coordination
What to Expect During a Routine Eye Exam
Visual Acuity Test: This test measures how well your child can see at various distances. Your child will read letters or symbols from a chart.
Eye Alignment and Movement Test: The eye doctor will check how well your child’s eyes work together and track moving objects.
Depth Perception Test: This test assesses your child’s ability to perceive depth and see in three dimensions.
Color Vision Test: The eye doctor will check for color blindness using special charts or images.
Eye Health Examination: The eye doctor will examine the internal and external structures of your child’s eyes to check for any abnormalities or signs of disease.
Refraction Test: This test determines the correct prescription for eyeglasses or contact lenses if needed.
Tips for Maintaining Your Child’s Eye Health
Encourage Regular Breaks: Encourage your child to take breaks from screen time and near work (such as reading or homework) to reduce eye strain. The 20-20-20 rule is helpful: every 20 minutes, take a 20-second break and look at something 20 feet away.
Promote Outdoor Play: Spending time outdoors has been shown to reduce the risk of developing nearsightedness (myopia). Encourage your child to play outside regularly.
Ensure a Balanced Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids supports eye health. Foods like carrots, spinach, fish, and nuts are beneficial for maintaining good vision.
Teach Proper Eye Safety: Educate your child about eye safety and the importance of wearing protective eyewear during sports and activities that pose a risk of eye injury.
Monitor Screen Time: Limit your child’s screen time and ensure they use screens at a proper distance and angle to reduce eye strain. Encourage them to blink frequently to keep their eyes moist.
Keep Up with Regular Eye Exams: Follow the recommended schedule for routine eye exams and consult an eye doctor if you notice any signs of vision problems.
Conclusion
Routine eye exams are vital for ensuring your child’s vision health and overall development. By detecting vision problems early, preventing learning difficulties, and promoting healthy eye habits, you can help your child maintain clear vision and achieve their full potential. Remember to schedule regular eye exams and take proactive steps to support your child’s eye health.