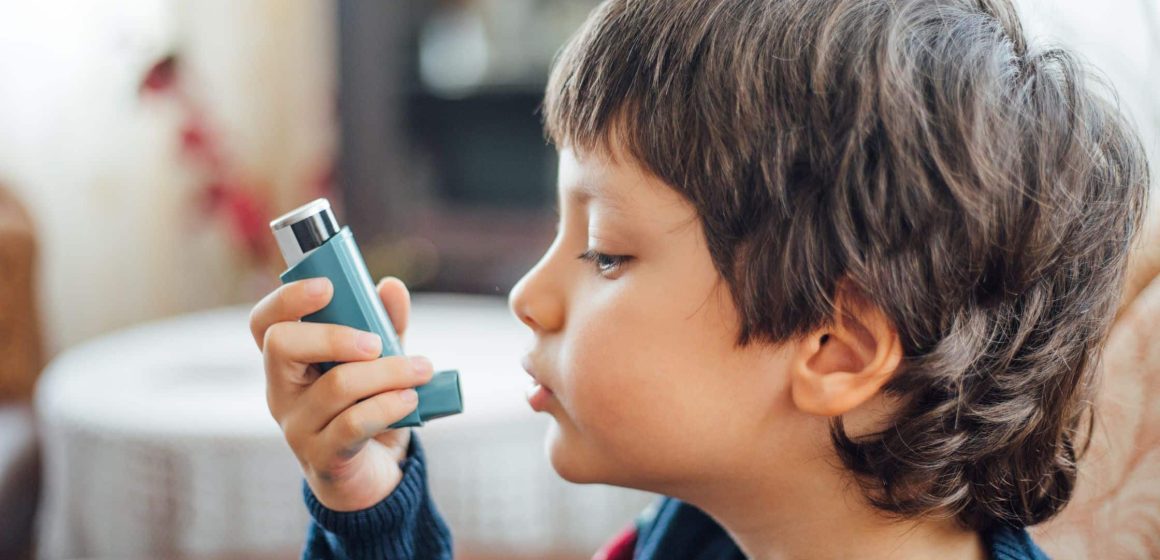
Asthma is one of the most common chronic conditions in children, affecting their ability to breathe and participate in everyday activities. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of asthma early and managing the condition effectively is crucial for maintaining your child’s health and well-being. This guide provides an overview of childhood asthma and offers strategies for coping with it.
Understanding Childhood Asthma
What is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, which leads to difficulty breathing. It can cause symptoms such as wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath.
- Common Triggers Asthma symptoms can be triggered by various factors, including:
- Allergens (pollen, dust mites, pet dander, mold)
- Respiratory infections (cold, flu)
- Physical activity
- Cold air or sudden weather changes
- Smoke (tobacco, wood)
- Strong odors or fumes
- Stress or emotional distress
Recognizing the Signs of Childhood Asthma
Common Symptoms
- Frequent coughing, especially at night, during exercise, or when laughing
- Wheezing or whistling sound when breathing
- Shortness of breath or rapid breathing
- Chest tightness or pain
- Fatigue or difficulty keeping up with physical activities
When to Seek Medical Help
If your child exhibits any of the following signs, seek medical attention immediately:
- Severe difficulty breathing
- Bluish tint to lips or face
- Severe coughing or wheezing that doesn’t improve with medication
- Difficulty speaking due to shortness of breath
Diagnosing Childhood Asthma
Medical History and Physical Exam
The pediatrician will take a detailed medical history and perform a physical examination to assess your child’s symptoms and overall health.
Lung Function Tests
Lung function tests, such as spirometry, measure how well your child’s lungs are working. These tests can help confirm an asthma diagnosis and determine its severity.
Allergy Testing
If allergies are suspected to be a trigger for your child’s asthma, the doctor may recommend allergy testing to identify specific allergens.
Managing Childhood Asthma
Creating an Asthma Action Plan Work with your child’s healthcare provider to develop a personalized asthma action plan. This plan should include:
- A list of your child’s asthma triggers
- Daily management strategies
- Instructions for using asthma medications
- Steps to take during an asthma attack
- Emergency contact information
Medication Management
Asthma medications are essential for controlling symptoms and preventing flare-ups. These include:
- Quick-Relief Medications: Also known as rescue inhalers, these medications (e.g., albuterol) provide fast relief during an asthma attack.
- Long-Term Control Medications: These medications (e.g., inhaled corticosteroids) are taken daily to reduce airway inflammation and prevent symptoms.
Avoiding Triggers
Identify and minimize exposure to asthma triggers. This may involve:
- Using allergen-proof covers on pillows and mattresses
- Keeping your home clean and free of dust and mold
- Using air purifiers to reduce indoor allergens
- Avoiding exposure to tobacco smoke and strong odors
- Managing outdoor activities during high pollen or pollution days
Monitoring Symptoms
Keep a symptom diary to track your child’s asthma symptoms and medication use. This can help you identify patterns and adjust the management plan as needed.
Regular Check-Ups
Schedule regular follow-up appointments with your child’s healthcare provider to monitor their asthma control and adjust medications if necessary.
Supporting Your Child
Educate and Empower
Educate your child about asthma and its management. Teach them how to recognize symptoms, use their inhaler correctly, and follow the asthma action plan.
Encourage Physical Activity
While physical activity can trigger asthma symptoms, it is essential for overall health. Work with your child’s healthcare provider to develop a plan that allows safe participation in physical activities.
Emotional Support
Living with asthma can be challenging for children. Provide emotional support and encourage open communication about their feelings and concerns. Consider joining a support group for families dealing with asthma.
Emergency Preparedness
Know the Signs of a Severe Asthma Attack Be prepared to recognize the signs of a severe asthma attack, including:
- Severe shortness of breath that doesn’t improve with quick-relief medication
- Inability to speak in full sentences
- Bluish color around the lips or face
Have an Emergency Plan
Ensure you and your child know what to do in case of a severe asthma attack. This includes when to use quick-relief medication and when to seek emergency medical help.
Conclusion
Managing childhood asthma involves a combination of medication, trigger avoidance, and regular monitoring. By working closely with your child’s healthcare provider and following an asthma action plan, you can help your child lead a healthy and active life despite their asthma. Education, support, and preparation are key components in effectively managing this condition.