Coping with Newborn Colic & Reflux: What Works & What Doesn’t
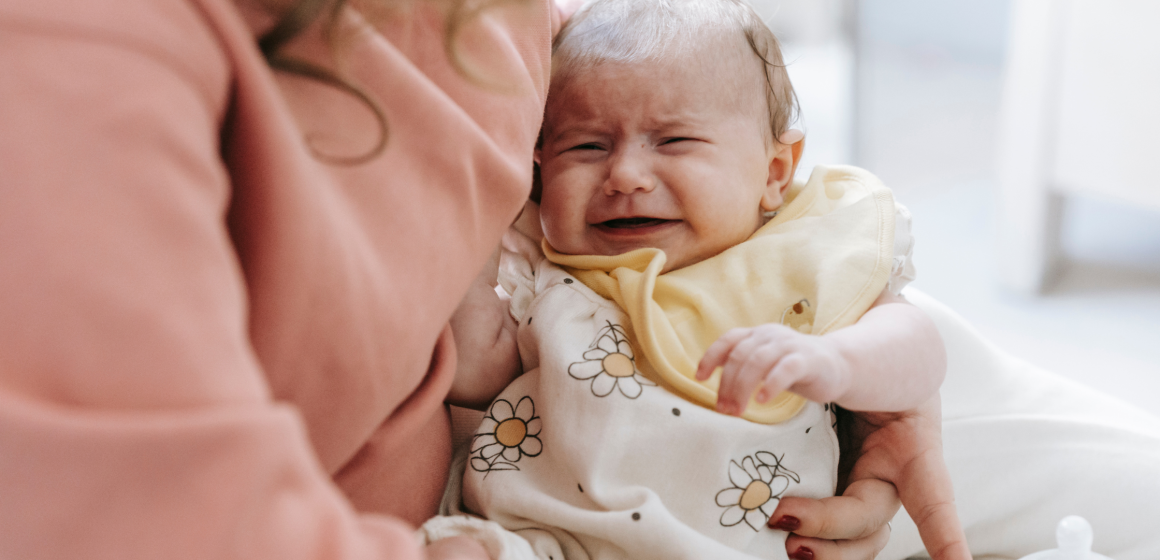
Every parent expects some crying, but when a baby cries for hours on end, it can feel overwhelming. Colic and reflux are two of the most common reasons newborns cry excessively, and they often leave parents feeling exhausted, anxious, and desperate for answers. Understanding what these conditions are—and what truly helps—can bring comfort and direction during those long days and nights.
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) reassures parents that both colic and reflux are common in healthy babies, usually resolve with time, and rarely cause long-term problems.
What is Colic?
Colic is defined as excessive crying that lasts more than three hours a day, at least three days a week, for more than three weeks, in an otherwise healthy baby. Colic usually begins around 2 to 3 weeks of age, peaks around 6 weeks, and improves by 3 to 4 months.
No one knows exactly what causes colic, but possibilities include sensitivity to stimulation, immature digestion, or normal variations in temperament.
What is Reflux?
Reflux occurs when stomach contents flow back into the esophagus, causing spit-up. Nearly all babies spit up occasionally, but reflux becomes a concern when it leads to poor weight gain, significant discomfort, or breathing problems. This more serious form is called gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
According to the AAP, mild reflux is common and usually improves as babies grow and their digestive systems mature.
What Works for Colic
Parents often try many strategies to soothe a colicky baby. Some approaches that may help include:
- Rhythmic motion: Rocking, swinging, or gentle car rides.
- White noise: Fans, vacuum cleaners, or sound machines can mimic womb-like sounds.
- Swaddling and soothing holds: Wrapping snugly or carrying the baby upright.
- Feeding changes: Smaller, more frequent feedings and careful burping.
Most importantly, know that colic will pass with time—even if it feels endless in the moment.
What Doesn’t Work for Colic
Despite many claims, there’s no proven “cure” for colic. Remedies like herbal teas, over-the-counter drops, or drastic formula changes rarely make a difference and may even be unsafe. The AAP advises parents to avoid untested remedies and focus on safe, comforting strategies.
What Helps with Reflux
For most babies with mild reflux, simple measures are enough:
- Holding the baby upright for 20–30 minutes after feeding.
- Feeding smaller amounts more often.
- Keeping the head slightly elevated during sleep (while still following safe sleep practices—never propping with pillows or wedges).
If reflux is severe—causing weight loss, frequent vomiting, or respiratory issues—your pediatrician may recommend further evaluation or treatment.
When to Call Your Pediatrician
Reach out to your pediatrician if your baby:
- Cries inconsolably for long stretches despite soothing.
- Spits up forcefully or vomits green or bloody material.
- Shows poor weight gain.
- Appears unusually sleepy, irritable, or unwell.
Your pediatrician can help determine whether the issue is colic, reflux, or something else, and guide you toward safe, effective solutions.
Caring for Yourself While Caring for Baby
Colic and reflux are hard not only on babies but also on parents. It’s okay to feel frustrated or overwhelmed. Take breaks when needed—place your baby safely in the crib and step away for a few minutes if you need to breathe. Reach out for help from your partner, family, or local support networks in Buffalo and Erie County.
The Bottom Line
Colic and reflux are tough, but they’re also temporary. With time, most babies outgrow both conditions, and supportive strategies help families get through the hardest weeks. Trust your instincts, lean on your pediatrician, and remember you’re not alone.
For more information, visit the AAP’s guide to colic and AAP’s reflux resources. For local care and support, connect with Medical Health Associates of WNY, where pediatricians partner with families through every challenge of early infancy.
Because while crying may feel endless, the support you need is always close by.